Effect of Intensive Blood Pressure Lowering on Kidney Tubule Injury: Findings From the ACCORD Trial Study Participants
- PMID: 30291011
- PMCID: PMC6309631
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.07.016
Effect of Intensive Blood Pressure Lowering on Kidney Tubule Injury: Findings From the ACCORD Trial Study Participants
Abstract
Rationale & objective: Random assignment to intensive blood pressure (BP) lowering (systolic BP<120mmHg) compared to a less intensive BP target (systolic BP<140mmHg) in the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes BP (ACCORD-BP) trial resulted in a more rapid decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Whether this reflects hemodynamic effects or intrinsic kidney damage is unknown.
Study design: Longitudinal analysis of a subgroup of clinical trial participants.
Settings & participants: A subgroup of 529 participants in ACCORD-BP.
Exposures: Urine biomarkers of tubular injury (kidney injury molecule 1, interleukin 18 [IL-18]), repair (human cartilage glycoprotein 39 [YKL-40]), and inflammation (monocyte chemoattractant protein 1) at baseline and year 2.
Outcomes: Changes in eGFR from baseline to 2 years.
Analytical approach: We compared changes in biomarker levels and eGFRs across participants treated to an intensive versus less intensive BP goal using analysis of covariance.
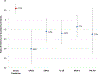
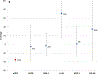
Results: Of 529 participants, 260 had been randomly assigned to the intensive and 269 to the standard BP arm. Mean age was 62±6.5 years and eGFR was 90mL/min/1.73m2. Baseline clinical characteristics, eGFRs, urinary albumin-creatinine ratios (ACRs), and urinary biomarker levels were similar across BP treatment groups. Compared to less intensive BP treatment, eGFR was 9.2mL/min/1.73m2 lower in the intensive BP treatment group at year 2. Despite the eGFR reduction, within this treatment group, ACR was 30% lower and 4 urinary biomarker levels were unchanged or lower at year 2. Also within this group, participants with the largest declines in eGFRs had greater reductions in urinary IL-18 and YKL-40 levels. In a subgroup analysis of participants developing incident chronic kidney disease (sustained 30% decline and eGFR<60mL/min/1.73m2; n=77), neither ACR nor 4 biomarker levels increased in the intensive treatment group, whereas the level of 1 biomarker, IL-18, increased in the less intensive treatment group.
Limitations: Few participants with advanced baseline chronic kidney disease. Comparisons across treatment groups do not represent comparisons of treatment arms created solely through randomization.
Conclusions: Among a subset of ACCORD-BP trial participants, intensive BP control was associated with reductions in eGFRs, but not with an increase in injury marker levels. These findings support that eGFR decline observed with intensive BP goals in ACCORD participants may predominantly reflect hemodynamic alterations.
Keywords: CKD progression; Chronic kidney disease (CKD); blood pressure (BP); eGFR decline; estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR); hemodynamics; hypertension; intensive BP control; kidney tubule; renal perfusion; tubular injury; urinary biomarkers; urine.
Copyright © 2018 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Estimated GFR Decline and Tubular Injury Biomarkers With Intensive Blood Pressure Control.Am J Kidney Dis. 2019 Jan;73(1):4-7. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.09.008. Epub 2018 Nov 10. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019. PMID: 30424915 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Effects of Intensive Blood Pressure Lowering on Kidney Tubule Injury in CKD: A Longitudinal Subgroup Analysis in SPRINT.Am J Kidney Dis. 2019 Jan;73(1):21-30. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.07.015. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019. PMID: 30291012 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Urine Markers of Kidney Tubule Cell Injury and Kidney Function Decline in SPRINT Trial Participants with CKD.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Mar 6;15(3):349-358. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02780319. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32111704 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney Damage Biomarkers and Incident Chronic Kidney Disease During Blood Pressure Reduction: A Case-Control Study.Ann Intern Med. 2018 Nov 6;169(9):610-618. doi: 10.7326/M18-1037. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Ann Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 30357395 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Meta-analysis of the Association of Estimated GFR, Albuminuria, Diabetes Mellitus, and Hypertension With Acute Kidney Injury.Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Oct;66(4):602-12. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2015.02.338. Epub 2015 May 11. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 25975964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between More Intensive vs Less Intensive Blood Pressure Lowering and Risk of Mortality in Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3 to 5: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Intern Med. 2017 Oct 1;177(10):1498-1505. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2017.4377. JAMA Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28873137 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by 14 articles
-
Chronic Kidney Disease and SGLT2 Inhibitors: A Review of the Evolving Treatment Landscape.Adv Ther. 2022 Jan;39(1):148-164. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01994-2. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 34846711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Blood pressure control in patients with chronic kidney disease.Korean J Intern Med. 2021 Jul;36(4):780-794. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2021.181. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Korean J Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 34153181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Promise of Tubule Biomarkers in Kidney Disease: A Review.Am J Kidney Dis. 2021 Nov;78(5):719-727. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.03.026. Epub 2021 May 27. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021. PMID: 34051308 Review.
-
Guideline-Driven Management of Hypertension: An Evidence-Based Update.Circ Res. 2021 Apr 2;128(7):827-846. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318083. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Circ Res. 2021. PMID: 33793326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in managing primary hypertension.Fac Rev. 2020 Nov 4;9:4. doi: 10.12703/b/9-4. eCollection 2020. Fac Rev. 2020. PMID: 33659936 Free PMC article. Review.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grant support
- Y01 HC001010/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079310/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- Y01 HC009035/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106962/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK096549/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95181/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95179/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95182/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95180/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95178/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK107908/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK090203/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC95183/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

