Personal access tokens (PATs) are an alternative to using passwords for authentication to GitHub when using the GitHub API or the command line.
If you want to use a PAT to access resources owned by an organization that uses SAML SSO, you must authorize the PAT. For more information, see "About authentication with SAML single sign-on" and "Authorizing a personal access token for use with SAML single sign-on."
As a security precaution, GitHub automatically removes personal access tokens that haven't been used in a year. To provide additional security, we highly recommend adding an expiration to your personal access tokens.
Creating a token
-
Verify your email address, if it hasn't been verified yet.
-
In the upper-right corner of any page, click your profile photo, then click Settings.

-
In the left sidebar, click Developer settings.

-
In the left sidebar, click Personal access tokens.
-
Click Generate new token.

-
Give your token a descriptive name.

-
To give your token an expiration, select the Expiration drop-down menu, then click a default or use the calendar picker.

-
Select the scopes, or permissions, you'd like to grant this token. To use your token to access repositories from the command line, select repo.
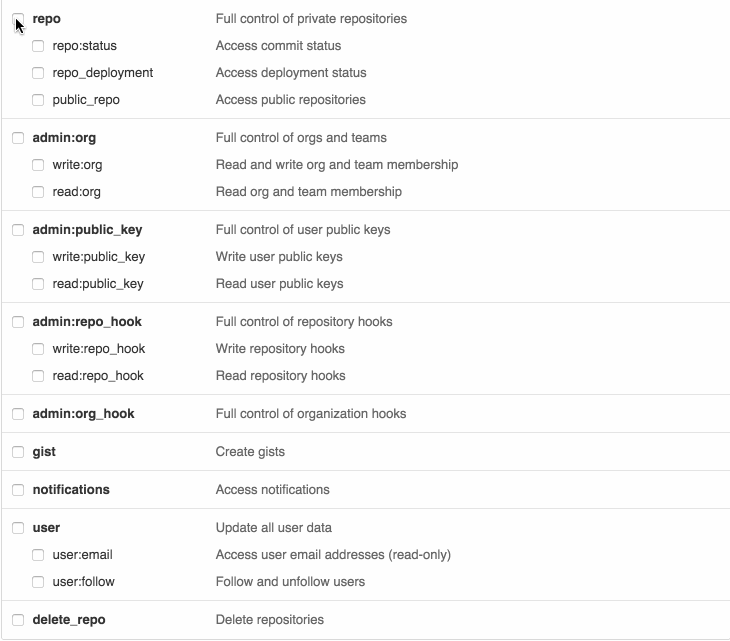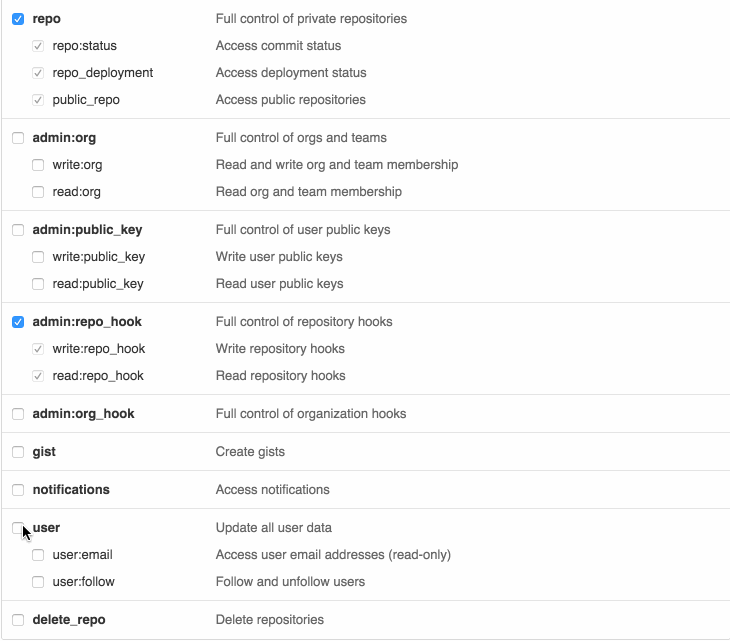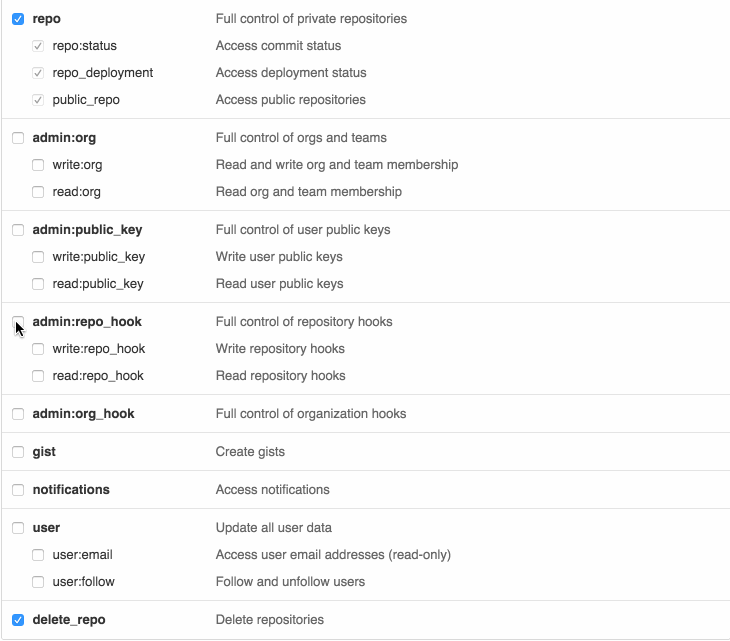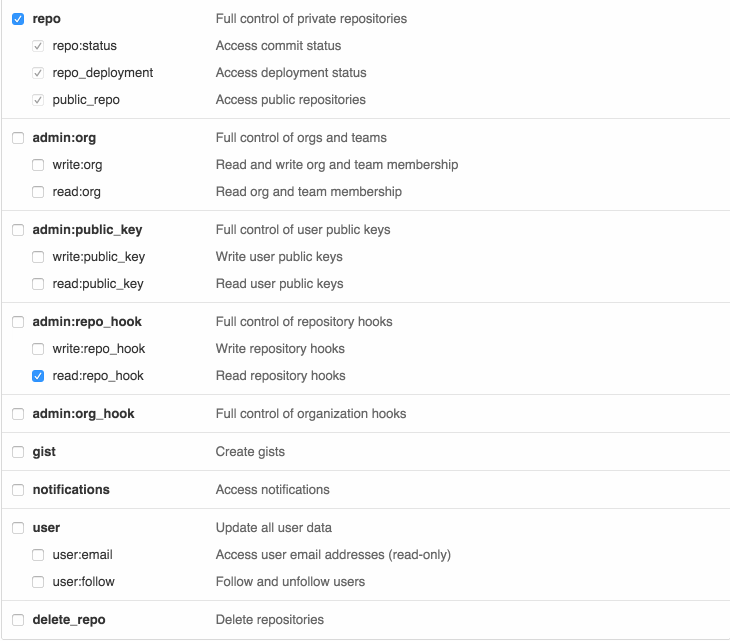
-
Click Generate token.

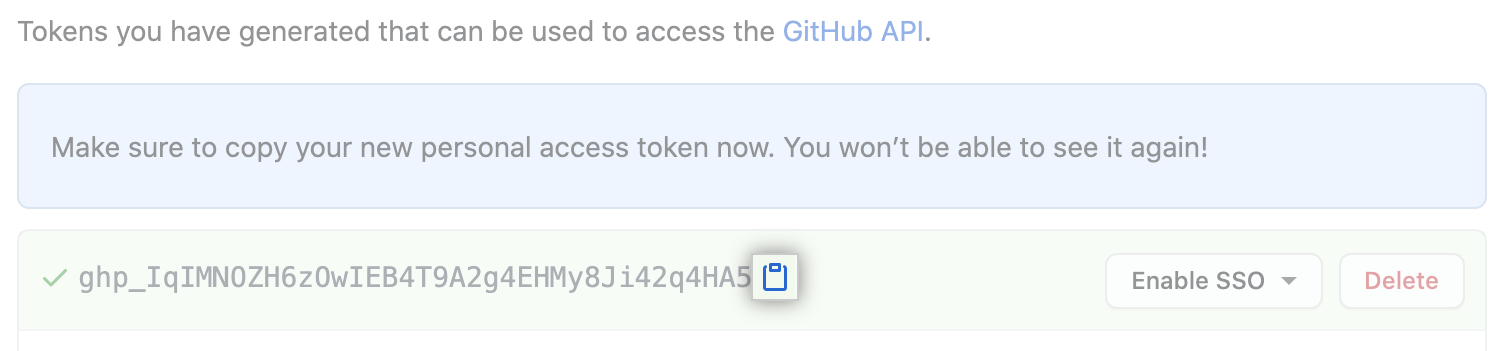
Warning: Treat your tokens like passwords and keep them secret. When working with the API, use tokens as environment variables instead of hardcoding them into your programs.
-
To use your token to authenticate to an organization that uses SAML SSO, authorize the token for use with a SAML single-sign-on organization.
Using a token on the command line
Once you have a token, you can enter it instead of your password when performing Git operations over HTTPS.
For example, on the command line you would enter the following:
$ git clone https://github.com/username/repo.git
Username: your_username
Password: your_tokenPersonal access tokens can only be used for HTTPS Git operations. If your repository uses an SSH remote URL, you will need to switch the remote from SSH to HTTPS.
If you are not prompted for your username and password, your credentials may be cached on your computer. You can update your credentials in the Keychain to replace your old password with the token.
Instead of manually entering your PAT for every HTTPS Git operation, you can cache your PAT with a Git client. Git will temporarily store your credentials in memory until an expiry interval has passed. You can also store the token in a plain text file that Git can read before every request. For more information, see "Caching your GitHub credentials in Git."