About commit email addresses
GitHub uses your commit email address to associate commits with your GitHub account. You can choose the email address that will be associated with the commits you push from the command line as well as web-based Git operations you make.
For web-based Git operations, you can set your commit email address on GitHub. For commits you push from the command line, you can set your commit email address in Git.
Any commits you made prior to changing your commit email address are still associated with your previous email address.
Note: You cannot verify email addresses from disposable email address services (services that allow you to receive email at a temporary address that expires after a certain time). If you'd like to keep your email address private, you can use a GitHub-provided noreply email address. For more information, see "Setting your commit email address on GitHub."
If you'd like to keep your personal email address private, you can use a GitHub-provided no-reply email address as your commit email address. To use your noreply email address for commits you push from the command line, use that email address when you set your commit email address in Git. To use your noreply address for web-based Git operations, set your commit email address on GitHub and choose to Keep my email address private.
You can also choose to block commits you push from the command line that expose your personal email address. For more information, see "Blocking command line pushes that expose your personal email."
To ensure that commits are attributed to you and appear in your contributions graph, use an email address that is connected to your GitHub account, or the noreply email address provided to you in your email settings. For more information, see "Adding an email address to your GitHub account."
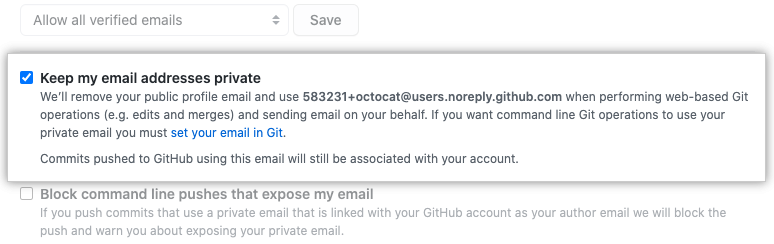
Note: If you created your GitHub account after July 18, 2017, your GitHub-provided no-reply email address is a seven-digit ID number and your username in the form of ID+username@users.noreply.github.com. If you created your GitHub account prior to July 18, 2017, your GitHub-provided no-reply email address is your username in the form of username@users.noreply.github.com. You can get an ID-based GitHub-provided no-reply email address by selecting (or deselecting and reselecting) Keep my email address private in your email settings.
If you use your GitHub-provided noreply email address to make commits and then change your username, those commits will not be associated with your GitHub account. This does not apply if you're using the ID-based GitHub-provided noreply address. For more information, see "Changing your GitHub username."
Setting your commit email address on GitHub
If you haven't enabled email address privacy, you can choose which verified email address to author changes with when you edit, delete, or create files or merge a pull request on GitHub. If you enabled email address privacy, then the commit author email address cannot be changed and is <username>@users.noreply.github.com by default.
-
In the upper-right corner of any page, click your profile photo, then click Settings.
-
In the left sidebar, click Emails.

-
In "Add email address", type your email address and click Add.
-
In the "Primary email address" list, select the email address you'd like to associate with your web-based Git operations.

-
To keep your email address private when performing web-based Git operations, click Keep my email addresses private.
Setting your commit email address in Git
You can use the git config command to change the email address you associate with your Git commits. The new email address you set will be visible in any future commits you push to GitHub from the command line. Any commits you made prior to changing your commit email address are still associated with your previous email address.
Setting your email address for every repository on your computer
- Open TerminalTerminalGit Bash.
- Set an email address in Git. You can use your GitHub-provided
no-replyemail address or any email address.$ git config --global user.email "[email protected]" - Confirm that you have set the email address correctly in Git:
$ git config --global user.email [email protected] - Add the email address to your account on GitHub, so that your commits are attributed to you and appear in your contributions graph. For more information, see "Adding an email address to your GitHub account."
Setting your email address for a single repository
GitHub uses the email address set in your local Git configuration to associate commits pushed from the command line with your GitHub account.
You can change the email address associated with commits you make in a single repository. This will override your global Git config settings in this one repository, but will not affect any other repositories.
- Open TerminalTerminalGit Bash.
- Change the current working directory to the local repository where you want to configure the email address that you associate with your Git commits.
- Set an email address in Git. You can use your GitHub-provided
no-replyemail address or any email address.$ git config user.email "[email protected]" - Confirm that you have set the email address correctly in Git:
$ git config user.email [email protected] - Add the email address to your account on GitHub, so that your commits are attributed to you and appear in your contributions graph. For more information, see "Adding an email address to your GitHub account."